Football games. Band practice.
Cramming for tests while still trying to get eight hours of sleep.
High school can be
overwhelming. On top of it all, there's also whole new set of lingo you have to
learn. There's the alphabet soup of AP, IB, and MLA. There's the tongue twister: extracurriculars.
But, don't worry: We've
got you covered. Whether you are an incoming freshman, a parent of a student, or
teacher or tutor trying to teach some life skills, here is a handy guide to
some essential words for a successful high school career.rubric
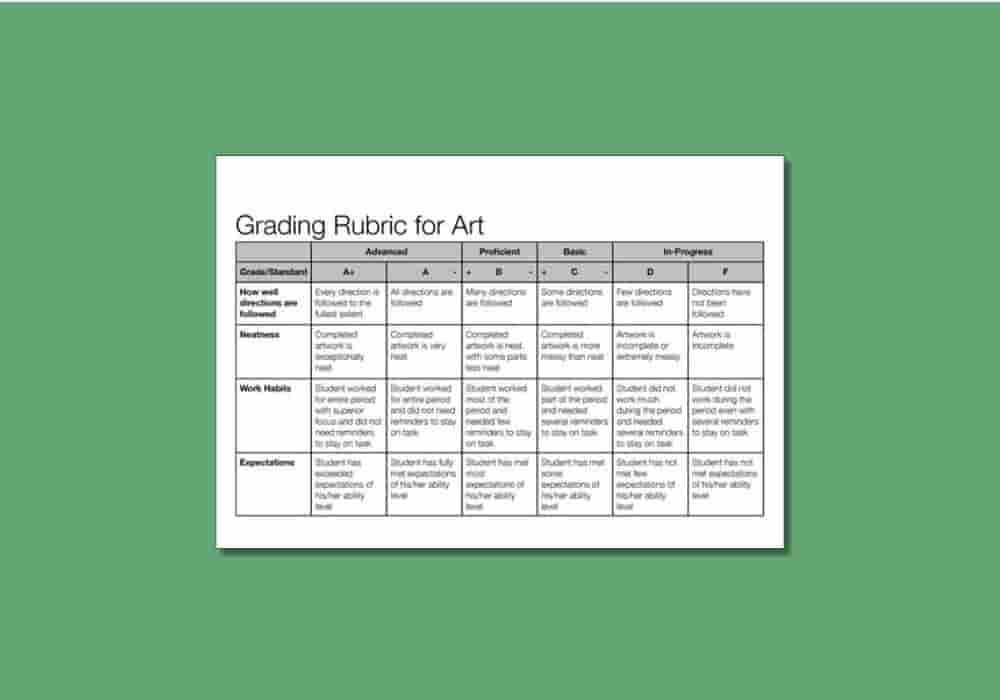 You will want to learn how to read a rubric carefully—or
else it will be covered in red marks! Funnily enough, this word actually comes
from the Latin ruber, meaning "red." Back in the Middle
Ages, rubrics were directions, traditionally written in red,
in church books about how to conduct a service.
You will want to learn how to read a rubric carefully—or
else it will be covered in red marks! Funnily enough, this word actually comes
from the Latin ruber, meaning "red." Back in the Middle
Ages, rubrics were directions, traditionally written in red,
in church books about how to conduct a service.
In education, a rubric is guide
that may accompany major assignments. It outlines the points, the standards,
the performances — the criteria — you need
to meet in order to receive a certain grade.

thesis (statement)
Every good essay includes
a strong thesis (or thesis statement).
In academic writing, a thesis statement is generally a sentence or two that summarizes the main point that an
essay, research paper, or speech is making. It is typically located at the end
of the introductory paragraph(s).
Thesis
statements are kind of like roadmaps,
laying out for the reader/listener where the writer/speaker is headed (the
argument) and how they are going to get there (the evidence).
Generally, you are taught
not to begin a thesis with
"I believe" or "I think," as it is considered more
convincing to have a clear, concrete stance on your argument.
In writing research papers, sometimes you need
direct quotes from your sources. Other times, you need to paraphrase that
information.
Paraphrasing is restating
a test or passage in your own words. Consider this statement: "A robust
lexicon can help students navigate a variety of discourse environments."
You might paraphrase it as: "Having a well-developed
vocabulary can help you be successful in many different contexts."
Paraphrasing also indicates that you understand what you are reading.
Remember: Even when paraphrasing,
you need to cite the source you got the information from, even if you are not
directly quoting it. Otherwise, you may be accused of ...
plagiarism
Plagiarism is a serious
offense. It is the act of using or imitating other words—or ideas—from another
source without citing that source. (Its origin is a Latin word meaning
"kidnapper.")
That's why giving credit to your source in
paraphrasing is so important. When we paraphrase, we may use our own words, but
we did not develop the original ideas.
If someone is caught plagiarizing,
they could fail the assignment, be suspended, or even get expelled from school.
Serious stuff.
There are computer programs that can
detect plagiarism, and your teacher may use them. Beware!
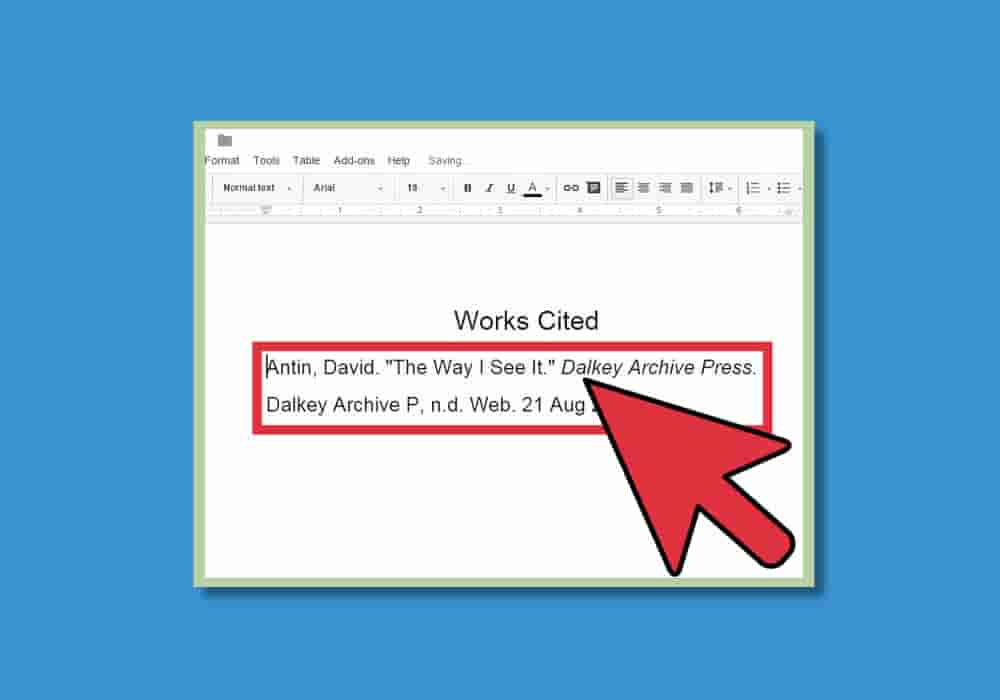
citations
Speaking of all this citing, what
are citations?
Citations are the act
of indicating where you got your information from in an essay or research
paper. These can include books, reputable websites, newspapers, academic
journals, and images.
In-text citations are shorthand
indications that appear in the body of your text. The "Works Cited"
(bibliography) page is a compilation of all the sources you used, and appears
at the end of the document.
There are different citation styles, so it's
important to verify which style your teacher uses. One major one in the
humanities (e.g., English, Social Studies) is MLA. Cue next
slide.
 MLA
MLA
MLA stands for the Modern Language Association. This organization
publishes a style manual that is often the first writing and research style
students learn in high school, especially in English class.
 MLA style provides writers with a system for cross-referencing their sources from their
parenthetical references (the in-text citations) to their “Works Cited” page
(the bibliography). This cross-referencing system allows readers to locate the
publication information
MLA style provides writers with a system for cross-referencing their sources from their
parenthetical references (the in-text citations) to their “Works Cited” page
(the bibliography). This cross-referencing system allows readers to locate the
publication information
of the source material.
elective course
This is where you get to have fun and explore!
Elective courses are classes you can take outside of your core requirements (math,
science, language arts) for graduation. These classes are still extremely
valuable for learning more about an area of interest. Examples of electives include
a foreign language, music, visual art, and drama classes.
They are called elective because you
elect, or "choose," which you want to take them (or, in some cases,
if you take them at all). Taking varied elective courses throughout
your time in high school is a good way to test out what your major could be in
college.
extracurriculars
Extracurriculars are
another great way to learn about a subject or skill. The word extracurricular itself means
"outside of the regular curriculum." Debate, student government,
volunteer groups, and athletics are typical extracurriculars.
In addition to adding an enriching experience to
your education, they look impressive on college applications, even though you
don't typically earn credit toward graduation from them.
Advanced
Placement | International Baccalaureate
Both of these are
accelerated programs for students who would like more of a challenge.
Advanced Placement, or AP, courses, offer a college-level
experience for those still in high school. Students are required to take an
end-of-year examination and may be awarded college credit (at the institution
they attend) for the course if they pass.
Subjects are offered in a
range of subjects, from Art History to Latin to Calculus, and students often
take them in their junior and senior years.
The International Baccalaureate (IB),
founded in 1968 in Sweden, offers a variety of programs for students around the
world. These programs go beyond just traditional academics and emphasize
philosophy and community service, preparing students to be leaders and citizens
of the world. Students can earn college credit and even an IB diploma.
Dual enrollment is offered by many high schools in
conjunction with local community and technical colleges.
Some students prefer to
do this instead of taking typical elective courses. With dual enrollment, students can
take certain college classes at a postsecondary institution while still in high
school, hence the term dual (meaning "two, double") enrollment.
Dual enrollment opportunities can be an important step
for students who wish to get a jump start on one of the next steps after high
school: college, which has its own set of ... you guessed it, words to learn.







Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий